As we now know, there are many types of inverters available in the market, with different outputs and a wide variety of power ratings. So the next question arises of deciding which type to choose for your needs or which type of inverter to buy?
That’s what Nasir is going to explain for this new part of his tutorial about Inverters.
When such a large variety is available in the market, it becomes more and more difficult to choose from them. So a complete guidance becomes really necessary in such cases.
Choosing a Sine Wave inverter
So the first step is to define your needs, i.e. decide that for which equipment you need an inverter. If the equipment is sensitive, then it would require a pure sinusoidal voltage to operate on. This means we would have to use a pure sine wave inverter, so that it generates a pure sine wave for the equipment to operate on.
Since there is some equipment which only operates properly on true sine wave like digital clocks, variable speed motors etc, so for this type of equipment, pure sine wave inverters are the best option to use.
Choosing Modified Sine Wave inverters
Contrary to this, there is some equipment which can accept a bit of voltage fluctuations and would not undergo any damage in case a continuous voltage or pure sinusoidal voltage is not supplied to them. For such type of equipment, we can use a modified sine wave or quasi square wave inverters.
The main advantage of using modified sine wave inverters is that they provide such power at a very economical price, as compared to pure sine wave inverters, which are a bit expensive. The installation and usage of modified sine wave inverters is also easy compared to pure sine wave inverters.
The only drawback is that power fluctuations occur and a pure continuous sine wave is not available at the output.
Calculating Power ratings and capacity
Now, one more thought to ponder over- Among these types of inverters, there are many sub classifications as well. These sub types differ due to different power ratings, inverter’s capacity, and the capacity of the battery and the ratings of the equipment with which we have to use the inverter.
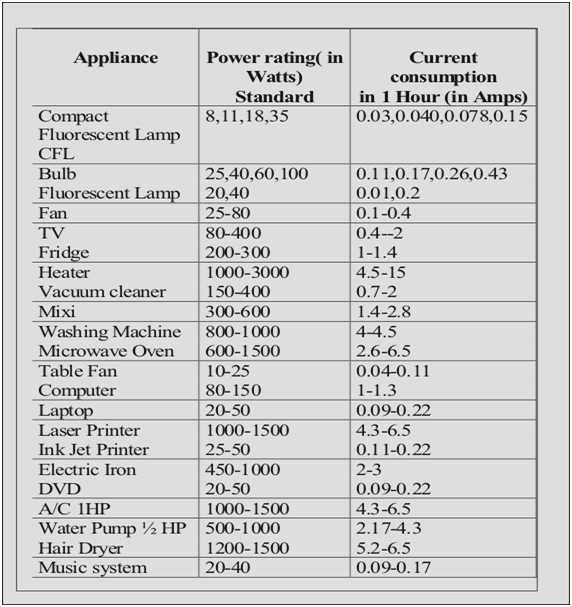
So the next step is to calculate your power need and decide accordingly the power rating of the inverter you want. This can be done easily, by adding up the total power of the total load with which you have to use the inverter. The power ratings of different everyday use equipment are shown in the table below:
After the power has been calculated, you can move on to calculating the inverter’s capacity. This can be done even more easily, but dividing the power rating by the power factor and getting the required result. Afterward, you can calculate the capacity of your battery by the following formula:
X Battery Capacity (in Ampere Hours)
Nasir.


what types of inverter are commonly used in industrial plant?
current (in amps) is not consumed, energy (kWh) is consumed. It is meaningless to say “current consumed in an hour.” Current is like speed in miles per hour. We do not say that our car consumes 50 miles per hour in one hour. Our car consumes a certain quantity of gas (energy) in one hour. It is correct to say that a certain quantity of Kilowatt hours (kWh) are consumed in 1 hour because kilowatt hours is a quantity of energy.
I don’t understand the formula, its a bit vague. can you simplify it a little plz