
Let’s read what your fellow electrical engineer Yasser has to say about it.
Every day, thousands of people face serious physical injury or even loss of life due to accidents at the workplace. Therefore the safety awareness to protect plant personnel and helping the organization to run the business without any hassles is critical.
Therefore, in this article we are going to talk about the importance of safety, the causes of accidents and the protection layers to prevent and mitigate the risks of accidents.

Fig. 1 Tchernobyl disaster
First to show the importance of safety, I will give you an example. In Ukraine, more than 30 years ago, the biggest industrial disaster at a nuclear power plant. The operators disconnected the protection systems for the sake of testing and commissioning of a run-down turbine generator. For a less than a minute, they broke the critical operational safety actions causing a nuclear disaster for years. This is one of the causes of accidents; human failure. Now let’s discuss the other causes.
There are 3 main causes of accidents:
- Human failures.
- Equipment failures.
- Random reasons; e.g. power loss, short circuit, faulty design, etc…
According to a research study, the human failure is the biggest cause with 39%, the random reasons comes second with 35% and the equipment failure with 26% at third place.
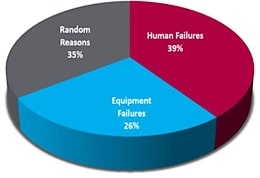
Fig. 2 a research study by TNO, a Dutch organization for appliance scientific research
Two main protection layers, prevention and mitigation, must be implemented to avoid the risks resulting from the causes mentioned.
- Prevention layers aim to reduce the probability of hazardous events including the process design, process control system, alarm system and safety instrumented system.
- Mitigation layers aim to decrease the severity of those hazardous events including physical protection, plant emergency response and community emergency response.
Now we will talk in detail about one of the layers; safety instrumented system or SIS.
Briefly, SIS prevents hazardous events. It requires 2 things:
- Functional requirements to define the function of the system.
- Performance requirements to define the efficiency and reliability of the SIS.
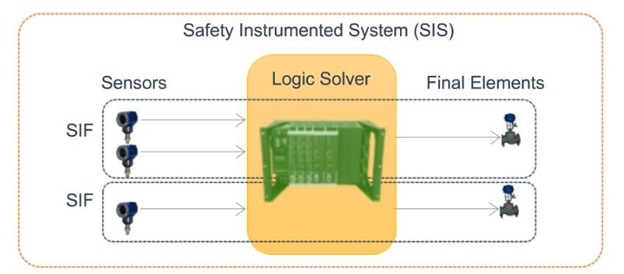
Fig. 3 Example of safety instrumented system
To good understand these requirements and learn how to define and apply them, then exploring the safety standards like IEC 61508 and IEC 61511 is a must as they ensure an acceptable safety integrity level for all safety instrumented functions of the system. This is of course out of our scope and it needs books not just articles.
To sum up, safety is not a something to bargain and remember one second without a safety may cause disasters.