Here’s an article by B.Q., one of the members of the Electrical Engineering Community. He kindly sent us this essay last week and we thought it would be nice to share it with you all! Want to be published too? Reach us by mail
By definition, “a circuit breaker is a protective device that operates automatically”. Certain fault conditions can actuate a circuit breaker resulting in a discontinuation of power supply to the relevant circuit or device.
Circuit breakers are an integral part of the electrical systems and their application differs with respect to the scenario. They are also used for planned electrical isolation of a system or equipment.
Circuit breaker: the Heart of Electrical Protection
Any Electrical protection system and the scheme are designed by the incorporation of several devices like Fuses, relays, CTs, PTs etc.
However, it is a circuit breaker that acts whenever a fault signal is picked and relayed by any sensing element. Whether it’s, overload, ground fault, under/over frequency, short circuit – the affected electrical system gets de-isolated by means of a CB.
Circuit Breaker Failure : which factors?
There are several factors which can lead a circuit breaker to a point where it becomes ineffective. MV and HV CBs often comes with electro-mechanical parts, motors, and other auxiliary equipment. Their internal mechanism requires proper maintenance for optimal performance. An eye should be kept on their wearing and tearing as well.
Following are some common factors which come with a potential of harming circuit breakers:
- Corrosive, moist and unfriendly operating environment
- Aging equipment
- Regular making and breaking of circuits
- Poor maintenance
- Mishandling during manual operation
Circuit Breaker Failure : which consequences?
Well, the operation of any electrical system with a faulty CB endangers the entire system and other associated load as well. In domestic systems, electrical fires are generally attributed to the failure of CBS. When it comes to the LV and HV systems the stakes are even higher.
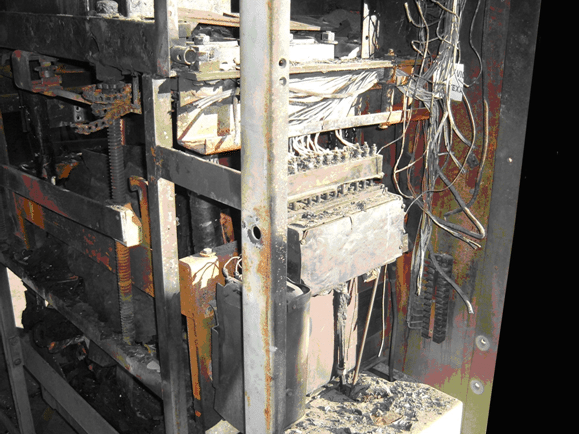

A failed circuit breaker often destroys entire electrical panel
A breaker that cannot perform and trip open as per the designed scheme could worsen up the situation. Overheating of a breaker could affect other breakers, instruments, and cables in the panel.
- Electrical Fires
- Destruction of the associated electrical equipment
- Tripping of the entire electrical source
- Production losses
- Injuries, fatalities

circuit breaker failure can make headlines
An example from the industry
Consider a medium voltage 400V electrical generator driven by a diesel engine and exporting power via Generator Circuit Breaker (GCB). Now in a case of an electrical fault, the generator should trip while initiating a trip command to the GCB. Here comes the crucial part;
In this case, if the Generator Circuit Breaker fails to trip open than the said generating unit will become a subject to the “Reverse Power”. Subsequently, active power will pass on to the windings resulting in its “motoring”. This phenomenon is quite dangerous and can cause severe mechanical damage to the prime mover which in our case is a diesel generator.
Consider these 10 good practices
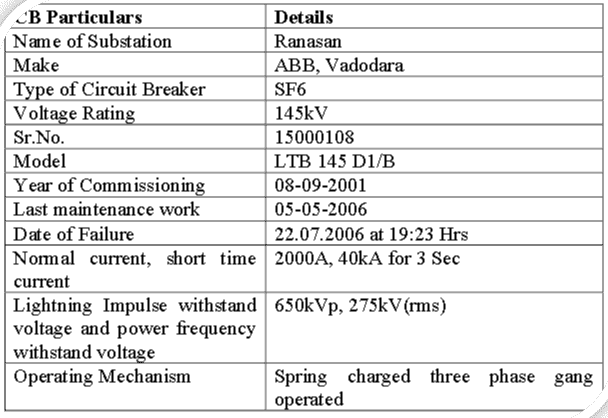
A model datasheet of an HV Circuit Breaker
- Never rack out breakers while on load
- Maintain required spares for prompt replacement
- LOTOTO protocol should be followed religiously
- Don’t reset any tripped breaker without root cause analysis
- Maintain a comprehensive record of CBs installed at your site
- Thermographic testing is recommended on always intact main incomers
- Don’t allow addition of load on the downstream of any CB beyond capacity
- If a breaker trips frequently than consider a thorough inspection of its internals
- Switching should be carried out by authorized and properly trained person only
- Comply with the vendor`s instructions about installation, operation, and maintenance of the circuit breakers
The Preventive Maintenance of CBs is a good idea!
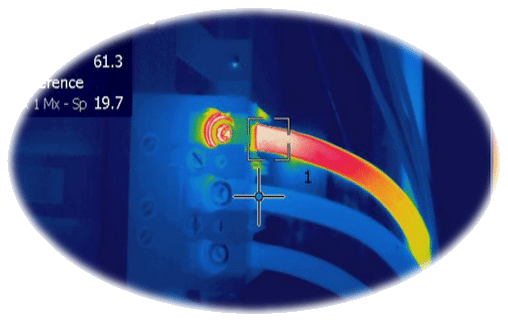
A hotspot observed through infrared thermography testing
As we all understand and acknowledge, circuit breakers do have a very critical role to play. We simply cannot rely upon degrading, faulty or erratic breakers as their one-time failure could lead us to destructive outcomes.
The preventive maintenance or routine maintenance enables us to ensure that the Circuit Breaker is healthy and ready to perform its Protective Function.
Let us share some of the most common tests recommended during the routine maintenance;
- Mechanical operation test
- Millivolt drop test
- Insulation resistance test
- Overload tripping test
- Connection test
Maintenance of CBs: important reminder
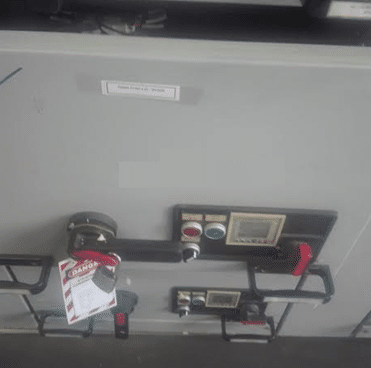
Maintenance work should never be considered on live circuits and online breakers. Visual inspections and infrared thermography, however, can be done on live systems. Always cut off the upstream source of power before starting your activity as shown in the image below;
Any maintenance activity on the equipment installed at the downstream of this breaker is safe because; it is properly racked out, logged and tagged out. There is no chance of an electrical shock or short in this case as the primary and secondary (source and load) terminals of this breaker are completely disengaged.
REMEMBER – some breakers are fed with a separate AC or DC control supply as well. A supervisor from the electrical team should make sure that there is no auxiliary supply intact before the commencement of the maintenance job.
Thanks for your attention,
B.Q.
Your thoughts on B.Q.’s first article for the blog? Share your impressions below!
The electrical circuits are very useful to provides electricity to plants. who is working on the field of electricity so they can taken some precautions and some times the circuits will be blasted by high voltage due to this effect the entire plant must be breakdown so to overcome these kind of problems, The plant must be runed in safety conditions.