Today we are going to talk about a very essential and popular item in every electrical system. Its importance spreads over power plants, houses and small apartments.
We can’t deliver electricity to any load without it; a circuit breaker. Therefore, Yasser one of the member of our community blog sent us this guide in which he hits some points regarding it. Enjoy!
Importance of Circuit Breakers
Circuit breakers are used in the following:
- In power plants and substations, they protect the main equipment from overloading, short circuit and thus, partial or total damage which costs very much.
- In branch circuits, they protect mainly the cables from overloading and breakdown also they protect the load from overloading in some cases.
- They protect you from leakage current in case of earth leakage circuit breakers. As in case you touched a live wire, the breaker senses the leakage current though your body to ground and then disconnects the circuit.
Types of circuit breakers
There are many types of CBs, here are some of them:
- Miniature Circuit Breaker: for low power applications and low short circuit level.
- Molded Case Circuit Breaker: can bear higher power up to 630 A and also can reach 100 kA as short circuit level.
- Air Circuit Breakers: used in many application in low voltage systems and is called Air as the insulating medium is Air.
- Vacuum Circuit Breaker: can bear higher voltages than the Air as it implements vacuum as the insulating medium and is used in medium voltage systems.
- Oil Circuit Breaker: used in medium and high voltage as oil is very robust insulating medium and has good capabilities in arc quenching.
- SF6 Circuit Breaker: the most common type and used in medium and high voltage due to the high dielectric strength of SF6, thermal stability and thermal conductivity.

Figure.1 (left): Air Circuit Breaker / Figure.2 (middle): Molded Case Circuit Breaker / Figure.3 (right): SF6 Circuit Breaker
As we briefly showed the common types of circuit breakers and where they are being used, now we will discuss how to select a circuit breaker on the scope of medium and low voltage. But to properly do such a thing you need to be aware of some aspects which are shown below.
- Load Classification:
- Trip Curve – it’s the relation between trip time and fault current and there are many types of them. Briefly they are:
1. Dynamic Load: the unique aspect regarding this type is the electro-magnetic field to operate. So obviously we are talking about motors and transformers which draw higher current than rated at starting.
2. Static Load: normally it draws the rated current when operating at full power and never draws more than it. It’s mainly the resistive load, such as heaters.
1. Type B: suitable for resistive loads as the magnetic trip time is at 5 times of the rated current.
2. Type C: suitable for most of loads as it combines the advantage of long time overload tripping and magnetic trip time is about 8 times of rated current.
3. Type B: suitable for resistive loads as the magnetic trip time is at 5 times of the rated current.
4. Type D: suitable for magnetic loads which have starting current so the breaker shouldn’t trip at the period of starting. The magnetic trip time is about 15 times of rated current.
5. For molded case circuit breakers and other types, trip curve can be modified by setting some values to control the overload protection and magnetic trip.
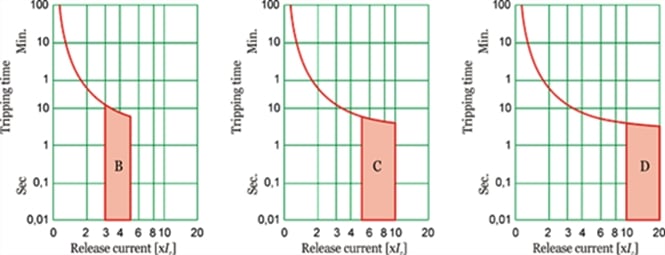
Figure.4: Trip Curves of Circuit Breaker
Steps to Select a Circuit Breaker
- Determine load type to know which breaker suits your application.
- In case of loads with starting current you should consider the circuit breaker magnetic trip current is higher than the starting current.
- In case of protecting sources (ex: UPS) you must select a breaker with the same value as source rated current.
- In case of protecting loads the circuit breaker rated current will be 1.25 times the load rated current to allow for overloading cases.
- Calculating the short circuit level at the circuit breaker is essential to determine its value so the breaker won’t fail in case of fault.
So after these short tips you are ready now to select the suitable breaker for your load or source. It’s very easy procedure, but must be done so as not to expose personnel to shocks or your devices to damage. Remember Safety comes first.
Do you have more tips to share with us? If you do, please share them in the comments.
Hi, Thanks For Sharing this Article. This article is very attractive and informational. And it also helpful for everyone to know about how to selection tips regarding Circuit Breaker. As well as, These Services are very helpful & Informational for everyone.