Hey it’s Steven Mill, I haven’t been posting articles for a long time, but I’m back and today I want to tell you about voltage dips and which problem they cause. Hope you’ll enjoy it!
What is a Voltage Dip?
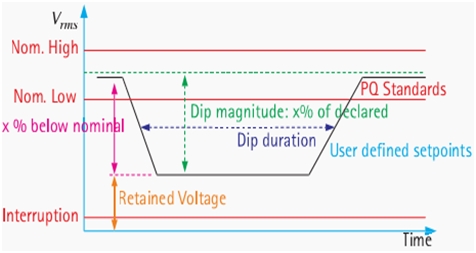
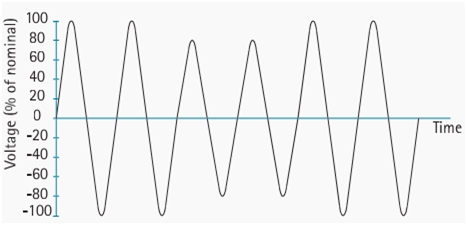
Under European Union standard EN 50160, the internationally adopted definition of voltage dip says that a voltage dip occurs when the power voltage drops below 90% of the standard voltage level for a minute or less. This decrease in RMS voltage, to be exact, lasts from half a cycle to several seconds.
A voltage dip is not a power interruption because power supply is not interrupted during its occurrence.
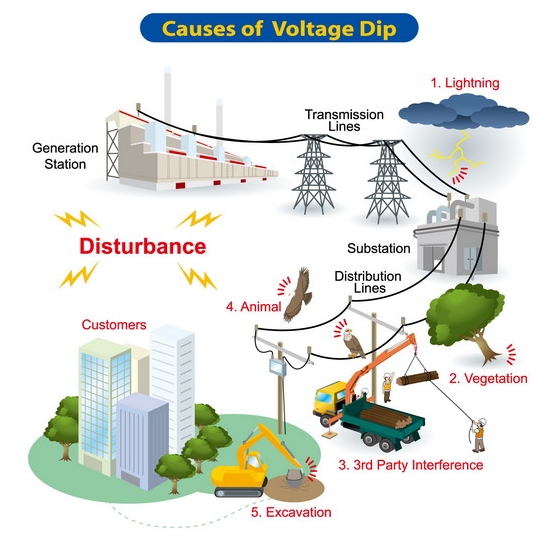
Causes of Voltage Dips
There are some reasons due to which voltage dips occurs. These are:
Momentary Loss of Supply
Sometimes the supply to a plant is temporarily cut off for a short time period. The electrical plant can be controlled to continue operation and maintain the process straightaway after the supply is restored. This type of voltage dip occurs because of the switching over from one supply source to another and Automatic Reclose (ARC) dead times.
Short Circuits
Voltage dips are also caused by faults on an electrical power system, for example, short circuits. A short circuit produces a large current to flow, which results in a voltage drop across the system loads. As the amount of energy drawn by a component is proportional to the square of the current, a short circuit also causes a large flow of current through a component, damaging it.
Short circuits usually result from overvoltage caused by lightning strikes or switching operations or also because of insulation collapse.
Load Switching
Partial voltage dips can occur because of load switching onto the supply. Major problems can be caused by large direct on line induction motors. When they are started, they can cause voltage dips. Electricity supply is affected when load switching takes place.
Network Switching
This usually happens in industries when the network is either switched on supply system or on the plant’s internal distribution network. If two different supplies which run at different load angles are paralleled, it will result in fast temporary change in voltage followed by a forceful situation before it is adjusted on a new stable load angle and everything is back to normal.
This momentary change is commonly fast and does not affect a normal plant. But if the plant is very sensitive to such change and voltage dips, its power electronic equipment is affected.
Power swings
Power swings can occur on the network when the supply network is weakened because of the severe faults on the supply network or the loss of transmission lines.
Impacts on Power Quality Problems
Mostly, a user’s power supply is not affected by a voltage dip but sometimes individual users may experience temporary dimming and flickering of their lights. There is no impact on the power equipment usually but very sensitive equipment’s protection device may be triggered causing it to trip. If the equipment is not harmed, it can be switched on again.
Elevators are designed to automatically switch back on when a voltage dip occurs. But for individual elevators that are affected, users can contact their suppliers to take measures so that the elevators work properly in case of voltage dips.
Power dips usually have little impacts on home and other appliances. Only sensitive equipment is affected. The major impacts of voltage dips are on industrial equipment and their operations. Power quality is not compromised and if it is, then it is only momentary.
Impact on the Process
When a voltage dip occurs on the supply of an industrial plant, some parts of the plant reach to such a point where the process must be discontinued as a safety measure. So, the electrical supply equipment should be carefully arranged so that its shut down time should be minimized. Failed ARC of transmission lines can result in another voltage dip.
Impact on Low Voltage Equipment
The electrically held contractors of low voltage (LV) switch gear fall out during voltage dips. When the control voltage falls below 70% of its standard value, the contractor opens and as a result the seal-in contact also opens. So, the low voltage drives stop working when a voltage dip occurs.
Variable Speed Drives
All types of variable speed drives do not work properly during a voltage dip. The operation of firing circuits which control power electronics cannot be sustained when the voltage drops to a low level. Therefore, the drive must be stopped.
Conclusion
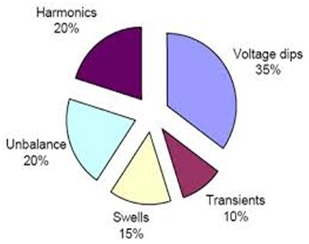
Any electrical system is susceptible to short circuits, electric heaters turning on, motors starting or abrupt increases in source impedance. Voltage dips are the most common power disturbance especially at industrial sites. They can arrive from the utility but mostly they are generated inside a building.
The power quality is affected by voltage dips and can harm the sensitive electrical equipment. This may lead to partial or complete interruption of a customer’s power supply but usually voltage dips occur within a few seconds and does not make a very big change.
Are there any other impacts of volage dips you have in mind? Let’s talk about it!
Steven Mill.