Smart grids have been talked about for as long as 1998 but 2005 was when the real work on smart grids started. Smart grid can be defined functionally, on technological basis and also on benefit-oriented basis.
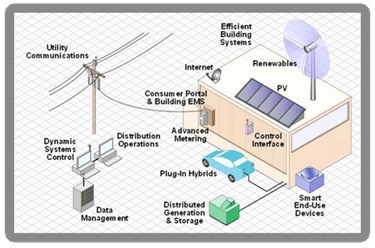
However the main idea on the word can be understood from the fact that smart grid is the use of the digital process data and communications data in the power grid so that the smart grid becomes the basis of information management and data flow. Using digital technologies in the power grids and the continuous input of new data into the system is what makes smart grids design so popular.
Transformations are nowadays found of three types. The first is the strong grid which involves the improvements required in the infrastructure of the system. The next is the smart grid whose core is the addition of a digital layer. The last is the business process transformations, highly important because of its involvement in the capitalization on investments.
The system updates that have been done in the electric grid at the sub-station level and the use of automated distribution system, all comes under the shadow of smart grid. New works are also, however, being done.
Characteristics
Smart grid offers a complete solution for the problems being faced in the electrical supply. Smart grid has found to be equipped with a number of characteristics, a few of which are being mentioned below.
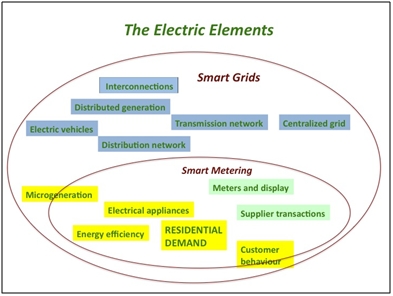
- Dependability: Fault detection and self- healing are the two very important features of smart grid. The supply as a result is un-interrupted and smooth, offering a consistent supply. A smart grid has multiple routes and is similar to a network of connections. This being helpful also leads to some problems. One of which is that if any line receives more voltage than its capacity then power failure will occur. This can be controlled through voltage reduction.
- Bi-direction energy flow: Previously used grids only allowed uni-directional flow of energy but smart grid offers bi-directional. This has been possible due to the advanced transmission methods and the automated distribution structure.
- Efficient: The technology used in smart grids has helped improving the infrastructure of energy transmission and distribution. The demand-side management property of the tech is a popular one. In this way decreased load falls on the transmission and distribution channels. What happens in case of load adjustment is that when the load on the distribution lines increases smart grid sends a warning to those channels utilizing the maximum energy. This is a sign for them to switch to backup generators. This reduces the load on the lines.
- Sustainable: Smart grids are more sustainable than the old grids because of its improved flexibility. Other renewable energy resources like solar power and wind power can also be used because of this fact. Disturbance in the calm weather also causes disturbance in the distribution channels failing them to maintain a stable supply posing an even greater challenge for the engineers.
- Customer friendly: Smart grid technology helps keep both the suppliers and the customers happy. Increasing the energy price strategy works for the suppliers as the load remains less during peak hours. The same goes for the customers who have then to pay less for less consumption during those hours. Generators are mostly used by the customers during those hours.
To reduce the consumption of energy during peak time something known as peak leveling is employed. The price of the energy is increased during the peak hours of energy usage and decreased during less usage hours. The customers are informed of the prices. The customers then use less energy during peak hours so the load is automatically reduced on the lines.
Future perspectives
Continuous research is going on smart grids to improve the tech further. Many projects have been initiated on these lines. Some major programs in line include IntelliGrid, Modern Grid Initiative (MGI), Grid 2030, GridWise, GridWise Architecture Council (GWAC) and GridWorks.
All these programs are involved in funding R&D, in developing a communication network between the various bodies involved in the energy sector including the suppliers, customers, researchers, educational institutes and government agencies and to improve the transmission, generation, storage and end-use of energy.
Smart Grid Modeling
Smart grid modeling is a very complex process and cannot yet be defined to be a specific process. Its relation has been found with ecology, human cognition, glass dynamics, information theory, cloud microphysics and many others. Analysis have been done in which they have been compared to complex biological systems, neural networks, to Kuramoto model, random fuse networks and entropy.
Reserves on smart grids
People have shown some reservations in the usage of smart grids. Like,
- How the data that they are providing will be used.
- Whether or not the electricity would still be available as per schedule.
- The price system becomes complicated and unable for the customer to understand which can lead to its violation by the supplier.
- The government will be in control of all the system and can use it as they demand.
Another very genuine concern is of the infrastructure security with regards to cybercrime. The communications tech being used in smart grid can be very easily manipulated through this way.
People can also manipulate the tech to steal electricity by altering the meter to report less energy consumption and vice versa.
See you on next tuesday for the second part of this article about Smart grids.

Preparation is easy: For each sandwich you take
2 pieces of buttered whole wheat bread, place a
slice of cheese between each piece and lay the sandwiches in a shallow cooking
dish. The conveyor pizza oven allows the baker to easily adjust time and temperature settings
to accommodate different specifications. ”
They do something to change it to make it more appealing to the buyer.