What is a Power Cable
Power cables are widely used in the electrical distribution system. A power cable is essentially a current carrying conductor which is enclosed within an insulation system and protective coverings and other special features as desired.
The conductors inside are stranded and the cable is flexible to be wound or bent as per requirements.
Applications
Power cables are used for a wide range of applications in the electrical distribution system such as:
- Connection between Transformer and switchgear
- Connection between Switchgear and individual load
- Connection between Generator and transformer
- Underground cables for utility distribution network in Urban areas
- Submarine cables for transmission purpose
- Cables in Ships, Wind mills, Buildings
Voltage Ranges Supported
Power cables are mainly used for:
- Low Voltages (LV) < 1 kV
- Medium Voltages (MV) > 1 kV and < 33 kV
However, power cables are sometimes also used for Extra High Voltage (EHV) up to 400 kV.
Factors determining Cable Types
There are several different types / configurations of power cables available in the market.
Each different type is determined mainly on the basis of following main factors:
- Conductor Type: Copper or Aluminum
- Conductor Configuration: Strands of conductors and no. of conductors (cores) single core, two / three / four core
- Type of Insulation
- Shielding material used
- Other special material: Like fillers, screens, material for special applications
Insulating Material in Power cables
The insulating material used in power cables has seen change over the years. In early periods before 1970s the cables were provided with paper insulations.
However, with growing technological advances in material science, improved synthetic insulating materials based on thermoplastic, Thermosetting, Fluorocarbon material have been discovered. These materials are now being widely used in the construction of a Power cable.
Following is the list of commonly used synthetic compounds found as Insulating material:
- EPR: Ethylene Propylene Rubber
- HEPR: Hard Ethylene Propylene Rubber
- PVC: Polyvinyl Chloride
- PE: Polyethylene – not so much in use due to its failure rate and short life
- PTFE: Poly Tetra Fluoro Ethylene
- XLPE: Cross Linked Poly Ethylene(Most commonly used in LV/ MV power cable)
Construction of a Typical Power Cable
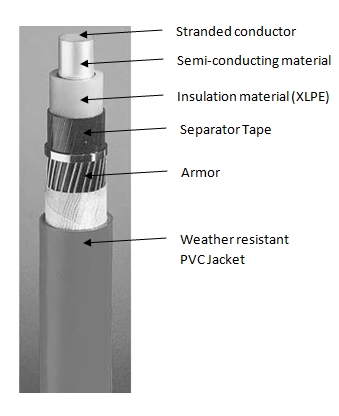
Figure below shows example of a single core XLPE insulated power cable.
As can be seen, at the center of it is stranded conductor. It is surrounded by a semi-conducting material to gradually reduce surface ionization.
The outer insulation covering is made up of suitable insulating material (XLPE or PE). It helps to withstand phase to earth voltage when the cable is laid underground. In case of a 3 core system, the three cores are separated from each other and placed in a common cable insulation system. An outer screening (usually made up of thin copper film) is provided to reduce the voltage stresses that may cause over the insulation.
An outer protective shield of armor (made of several metallic wires) is provided to protect the assembly inside from any type of mechanical wear / damage. The outermost covering is made of PVC jacket that provides protection to the whole cable assembly from weather conditions like sunlight, rain etc.
Conclusion
As seen, a power cable is a complex assembly that is designed with several different materials combined together to provide a cable that works perfectly in operation.
Each layer of material used in a cable has specific purpose in the design i.e. provide right level of current conductivity, right amount of insulation, right level of protection from mechanical, thermal, environmental conditions.
The choice of a particular type of cable depends on each individual application area and need to be appropriately chosen.
is there a truth that a clay can be as substitute for copper wire in christmas lights?