This article is the next and last part of Khuram’s article on underground MV/LV distribution systems. Enjoy and comment BELOW if you have any questions.
Underground electrical distribution is not only tidier but also less prone to environmental hazards as compared to the overhead distribution. Installation and maintenance cost, operational pros and cons, and a brief overview of cable structure are discussed in the previous part. Distribution transformers, switchgear and MV/LV cables are the main components of underground distribution system.
Structure and types of underground cables for a distribution system are discussed in this article.
Structure of underground cables
Basic construction of an underground cable comprises of the following:
- Conductor: Three cores of tinned copper or aluminum are used for three phase distribution system. Conductor is stranded to add flexibility and reduce skin effect.
- Insulation: Each core of the conductor is insulated to maintain a uniform electric field and minimize electrostatic stress. A suitable thickness of impregnated paper, PVC, vulcanized rubber, or XPLE (Cross linked polyethylene) is used depending on the voltage level.
- Metallic sheath: It is usually made of Lead or Aluminum and serves two purposes
(i) Sheath is earthed at one end, so it provides a return path to any leakage or fault currents;
(ii) It provides protection from moisture present in the soil or atmosphere. - Bedding: It is a fibrous protective layer surrounding the sheath, made of Hessian tape or Jute, works like a shock absorber and prevents mechanical injury.
- Armouring: One or two layers of galvanized steel wire or steel tape wound around bedding layer to provide protection against mechanical injury during installation and operation.
- Serving: It is the final layer made of jute or PVC. Serving keeps the armouring from corrosion and other atmospheric conditions.
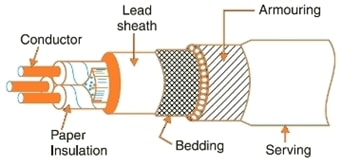
Basic Construction of underground cables
Types of MV/LV underground cables
Underground cables are either classified with respect to the maximum voltage carrying capacity or by the way of construction. Cable types with respect to voltage rating are as follows:
- Low tension cables have maximum voltage rating of 1000 V
- High tension cables have maximum voltage rating of 11KV
- Super tension cables have maximum voltage rating of 33KV
- Extra High tension cables have maximum voltage rating of 66KV.
Underground cables have variations from basic construction for different usages. Classification based on the cable construction incorporates the following:
- Belted Cable: A layer of oil impregnated paper is used to insulate the conductors. This type of cable is employed for voltage levels up to 11KV.
- Screened Cable: H-Type screened cables have the cores insulated with paper and a perforated metallic layer (usually copper). SL- Type screened cables have lead sheath around each core of the conductor. Screened type cables are used for voltages up to 66KV.
Pressure Cable: Pressurized oil or pressurized gas (usually dry nitrogen) is circulated in these cables to withstand higher levels of electrostatic stresses. Such cables are used for voltage levels greater than 66 KV.
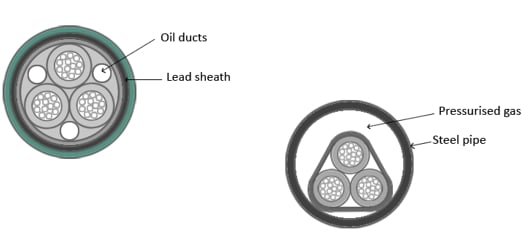
Underground cables – Pressure Cables
Thanks for reading my 2-parts article dear colleagues. Do not hesitate to ask me anything in the comments.
Khuram.
Excellent! Informative!! I am glad while searching i found the post, all the information is qualitative and helpful to grow my business. Top Tips!!