Today we’re glad to show you this article by A.N, our fellow member of the community. You still can send us your essays by mail. Enjoy!
Load shedding in electrical supply networks is a controlled process in which the utility company drops off part of the load in order to balance the demand and the generated capacity. This is often done whenever there is excess load on the system. In standby generators, it involves disconnecting or shedding some circuits to prevent an overload condition.

Figure 1: turning off some loads | image: infopakistan.pk
Power companies are required to supply sufficient energy to meet installed capacity. However, the demand may become inconsistent during peak periods. Whenever the power generated is insufficient to support the load, the electrical supply and distribution system becomes unbalanced and unstable.
If not controlled, the system can collapse and cause a total blackout. In such a situation, it may take hours or days to restore back the power. The utility monitors their systems and compare the load against the supply. If the difference between the two gets very narrow, some of the sections are disconnected so as to prevent the system from becoming unstable.
Effect of excess load on power generating equipment
In power systems, an excess load puts a stress on the generating equipment. It slows down the prime movers, associated generators and other parts of the system as they attempt to cope with the excess load. This leads to a combination of events including power swings and overloads which can cause the system becoming unstable. Some of the parts such as protection systems may interrupt the supply due to the excess current resulting from the overload.
The higher load may also lead to a lower generating and supply frequency. Even though the hydro generating systems can tolerate up to 10% frequency change, the thermal generator’s operation will be affected since they are more sensitive. A five percent decrease can reduce the generated power significantly due a decrease in the energy to the turbine generator.
The reduced frequency can damage the steam turbines as well as the frequency sensitive load. As such, most generator systems incorporate under-frequency relays to automatically disconnect some of the excess load.
Why the electrical supply capacity is less than demand
The causes of insufficient electric energy are numerous and ranges from increased developments, policy issues, technical issues, management, corruption and inefficiencies and more.
Inefficiency and lack of maintenance of generating and distribution systems
Lack of maintenance of the generating and distribution systems as well as other factors may lead to malfunctioning generators and losses in transmission and distribution systems, leading to significant power losses. This leads to low output which cannot cope with the installed load. However, if the systems are well maintained and losses minimized, the losses can supply extra load.
Other factors that will cause installed capacity to deliver less power are lack of skilled labor, use of outdated facilities and installations that degrade the delivery of the power to consumers.
Increased population
With urbanization and over-reliance on technology, the demand for electricity increases rapidly and the generating companies must increase the supply to keep up with the demand. If this does not happen, the load may exceed the supply and cause instabilities.
Improved living standards
When people get access to more income, their improved living standards allows them to use more electricity. They require services that rely on electricity as well as acquiring more electrical appliances for the home, in addition to using more gods which directly means that manufacturers must use more energy to produce the goods.
Lack of planning
If the generating companies haven’t factored in future growth, it becomes a challenge to meet an unexpected increase in demand. The load shedding could probably be used temporarily, but it becomes a problem if nothing is done to improve capacity and instead turn to the shedding as a permanent solution.
Load shedding procedures
- Utility companies use scheduled load shedding so that the available electricity is fairly shared by the consumers. This involves switching off some parts of the electricity supply network in a planned and controlled process. They alternate between different parts and time schedules to ensure that at least everyone gets power at a specific time. By dropping off the excess load, the power system remains stable.
- Some smaller generators such as those used in domestic applications have inbuilt load shedding capabilities. This becomes necessary when these are used as standby generators, in the event of a utility power outage, the emergency supply kicks in. And since all the circuits and appliances are connected, the load demand may exceed the generator capacity. When the load becomes too much, the generator sheds some of the smaller non-critical circuits automatically in an attempt to reduce the load.
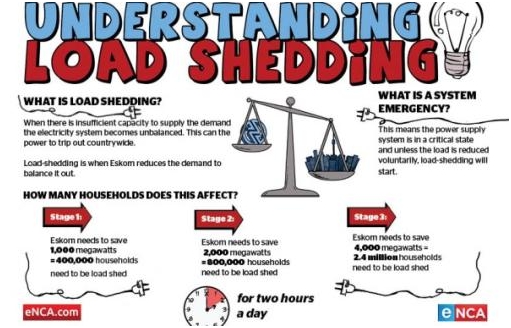
Figure 2: Understanding load shedding | image: enca.com
Advantages of load shedding
Load shedding impacts negatively on consumers and in particular the manufacturers and industries that rely on electricity.
- Prevents overloading and damage of the power generators
- Prevents instability and system collapse of the electrical generation and distribution systems
- Ensures that consumers or parts of the network have power as opposed to a total blackout.
- The planned schedules ensure that available capacity is shared fairly and each consumer gets power at one time or another.
- It serves as a warning to the utility hence forcing them to increase capacity, and efficiency so as to meet the demand.
Disadvantages of load shedding
- Loss of production
- Increased crime due to darkness and lack of jobs
- The utilities may not increased the output
- Restoring the load may cause more instabilities
Conclusion
Electrical load shedding is a method of reducing the demand on the electricity generation and achieved by switching off some loads or energy supply to some geographical areas. This is usually a last measure by the utilities, and often implemented to prevent overloading the generating systems and eventual collapse of the entire power system.
Load shedding is one of the last things that a utility company should look at. It leads to frustrated customers and loss of revenue for the consumers as production drops. In addition, it may cause equipment damage.
Electricity companies should ensure that they have enough capacity to meet normal and peak demands. This can be achieved by planning for future electricity demand and progressively upgrading the generating equipment, maintain existing systems, reducing transmission losses and increasing efficiency in the entire system.
A.N
Did it help? Tell us in the comments below!