In this article your fellow electrical engineer Yasser is going to explore the different types of relay and the devices that relays protect…
We used to consider circuit breakers as the devices that protect the electrical systems, however circuit breakers are only the muscles they just isolate and protect when they get the orders. Relays are the brains, the devices that sense the faults and compare the value to the predefined values, and send the signals to breakers to take the actions.
What is Relay?
First of all we need to define the relay. It’s the device that protects the electrical systems against abnormal conditions like over and under voltage, over load and short circuit to ensure the safety of equipment from damage and personnel from shocks.
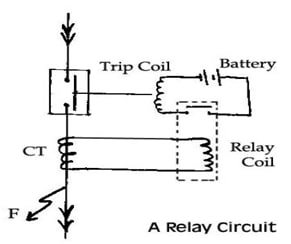
Figure.1 Relay circuit | ieeexplore.ieee.org
As shown in figure.1, the relay circuit is composed of a coil which senses the fault using the current transformer and then closes the electrical circuit of the trip coil to isolate the faulted part of the system.
Of course the relay must be fast, selective (can distinguish between faults in its area and those outside its area), reliable, simple and economical.
Classification of Relays
Relays are classified according to many things:
1. According to speed:
There are 2 kinds of relays instantaneous relay and time delay relay which waits some time before tripping action.
Also there’re 3 kinds of speed normal, high and ultra-high speed each is used depending on the application and the level of accuracy needed.
2. According to theory of operation:
- Attraction type relay – When the current passing in the coil exceeds the pickup value it attracts a contact to close the circuit.
- Induction type relay – When the current is induced in the coil a torque is produced to rotate the disc and connect the coils.
- Thermal relay – It consists of two metal strips with different thermal expansion when heated one is bended to close the contacts.
3. According to function:
- Directional relay – Detection of faults is done by measuring the phase displacement between the I and V.
- Earth fault relay – Detection of faults is done by measuring the current in the neutral line. It’s supposed to be zero as the vector summation of the three phase current is zero. So in the case of existence of current, this indicates an unbalance or current leakage.
- Distance relay – Using the impedance of the line, the ratio of its voltage and current, which is proportional to its length it can define the location of the fault through the line.
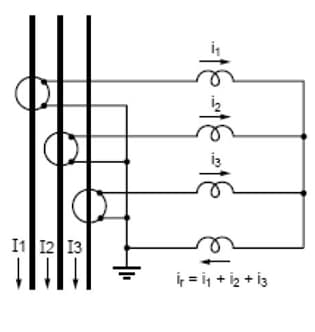
Figure.2 Using CTs to detect earth fault | scribd.com
We have just mentioned many kinds of relays and there are still many not mentioned each of them is used according to the application and the environment as we mentioned. Now we are going to mention some of the systems and equipment protected by relays and the techniques used.
Relays are used to protect feeder impedance and/or differential protection relays. While as for generators earth fault relays are used for stator, rotor and turns. In bus bars directional, distance, over current and earth fault relays are used. And finally for transformers over current relays are used, directional relays in the case of parallel transformers and differential relays are used for delta-star operation.
Briefly relays are so helpful for protection of different applications and now they are becoming digital using microprocessors which makes them faster and more accurate. So whatever the device you want to protect, there’s always a relay that suits it.
Yasser.
Do you have other tips to protect eletrical systems? How do you use relay to do so? Comment below!
Thanks..!! such a very nice information..