Before getting into details regarding the selection of busbars many questions should be answered first. What’s busbar? What’s the difference between busbar and feeder? Where is busbar used? What are the advantages and disadvantage of using busbars?
Let your fellow electrical engineer Yasser tell you more about it :)

Figure.1 Copper busbars in a distribution panel | image: dpfabs.co.uk
What’s busbar?
Let’s start with the definition. It’s an electrical conductor from whether copper or aluminum, copper is the most commonly used, carrying current at a specific voltage level used to distribute the electricity over many different circuits. The group of busbars are consisting of 5 bars, one for each phase, one for neutral and one for earth. The earth and neutral are 50% of the phase bars.
Where is busbar used?
Busbars are used in electrical panel boards to connect the incoming feeders to the outgoing feeders in distribution systems. Also it is used to connect high voltage and low voltage equipment.
What are the advantages and disadvantage of using busbars?
Busbars are easy to install, don’t need trays and they are cost effective especially when the ratings and distances increase.
However, in some arrangements of busbars, it requires extra protection which make the system expensive and the reliability of the system is badly effected when any of the bars are faulted.
Now we can move to the selection of the busbars.
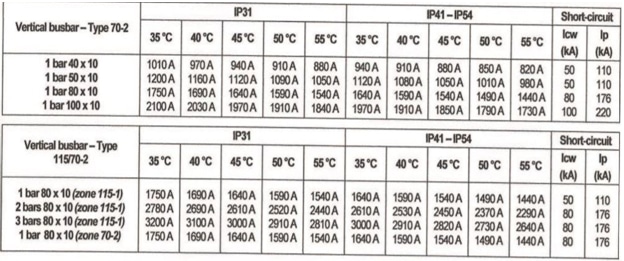
Figure. 2 Tables of busbars
Factors of selecting busbars:
- Position of the bars (Horizontal or Vertical)
- The current that busbar shall curry in normal operation.
- The rated short circuit withstand current that busbar shall withstand in fault condition.
- The rated peak withstand current that busbars shall withstand in case of lightning.
- The temperature of the atmosphere and the head dissipation of each component connected to the busbars.
- The Ingress Protection or the IP of the switchgear of the panel board containing the busbars.
- The number of sections or bundles per phase.
All the above values are used to select the proper basbars for a panel board. For example and using the tables above if the incoming circuit breaker is 2500 A Air Circuit Breaker ACB so the busbars of the three phase shall withstand this current in normal operation.
Getting back to the tables and assuming that the temperature is 40 ºC and the IP is 54 so two bars each 80*10 vertically for each phase will be the suitable option (They can withstand current up to 2530 A). As it’s also seen in the table it can withstand short circuit 80 KA and peak withstand current 176 KA)
Conclusion
The design of the busbars is flexible. You can start it from any of the giving data (e.g. if you want a specific short circuit level you can start from it moving to the current you want the bars to carry and then the dimension of the bars.
The installation of busbars also effects the current that bars can carry, but this out of the scope of this article. Finally, be very careful when you deal with busbars as they usually carry very high current that will kill you instantaneously.
your blogs contain very useful content. thanku for sharing busbar related information
Hi really informative blog, but can you have the blogs on ABS-2 Horizontal Tap to Horizontal Steel Surface or more like that product I just won’t in-depth info about the products Thanks.