New article by Martin M. who chose to highlight the 3 basic strategies for engineers and technicians at the industrial sites…You too can have your articles published by sending a mail to the team.
Introduction
The cost of investing in renewable energy sources is quite high. In addition, the costs of the main raw materials for electricity generation such as coal and oil are always rising. This means that the cost of electricity continues to increase despite the best of efforts.
Therefore, despite the long-term promises by the governments to reduce the cost of power, it is important that industries integrate short terms strategies to reduce peak power demand.
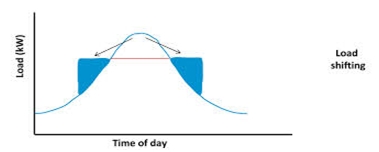
Load Shifting
A common contributor to high peak demand in industries is operating high demand processes at the same time. The solution is quite simple; shift the loads to ensure that the processes do not run together, and schedule the highest demand processes during the period that peak demand loads do not apply.
This, however, presents a list of conundrums, the primary of which is cost. Do note that power utility companies are out to make money. Therefore, the peak demand hours usually fall within the regular working hours. Load shifting thus may accrue some costs, which include overtime for the workers, as well as cost associated with hosting workers on site past regular working hours, such as security.
In other instances, the strategy may not work, especially due to conflicts between customer demand and regular provision of products and services.
Another problem associated with load shifting is operation interruption, especially in large manufacturing industries that depend on continuous processes.
Load shifting works best for batch type and short run manufacturers.
However, with a flexible work force, and different production units, load shifting can significantly reduce the peak demand, and thus, bills.
Power Factor Correction
This is perhaps the most widely used strategy to reduce peak demand. The common loads in industrial sites include induction furnaces, motors, ballasts, and the likes. Low power factor, in addition to penalties, leads to higher bills, as the industry has to pay for reactive as well as real power.
Considering the fact that off peak demands have lower rates, reduction of the power factor during this period will not have much effect on the bills. The primary objective is power factor correction during the peak demand period. This involves simply addition of capacitance through power factor correction units.
Overall Energy Efficiency
Efficiency intervention as a key strategy depends on the specifics of the method pursued. In electricity circles, energy efficiency primary means a significant reduction of real power consumption. This, unfortunately, means that you can reduce on energy usage without much impact on peak demand. The key objective is to reduce on the amount of power drawn during the peak demand period, rather than the total period of time, which includes low peak demand period.
On this note, the easiest way to instil energy efficiency during peak demand periods is proper equipment usage, insulation, as well as replacement of the standard equipment with high-efficiency types.
With industrial sites having to pay for the consumption as well as the right to have the right capacity available to them, it is important to integrate measure for reduction and monitoring. The above should work for a significant reduction of peak demand.
Considering that the demand charge is billed on the maximum peak demand for the month, by reducing on the peak demand amount, it is then possible to reduce the charge.
Martin M.