Introduction
Use of Shunt capacitors in a High Tension (HT) or Low Tension (LT) installation has become a necessity and also mandated by most of the utilities worldwide. Let us understand some concepts behind the use of a Shunt Capacitor.
Need for Capacitor Installation
There is a growing need for energy conservation and all efforts are being made towards the same. On the other hand, the electrical loads in almost all categories of customers i.e. Industrial, Commercial, Residential, Agricultural are inductive loads in nature.
These inductive loads include: electrical equipments and devices like: Induction Motors, Fans, Industrial A.C. machines. With the advent of technology and greater level of automation in the last few decades, the electrical load mix is greatly becoming Inductive in nature.
The drawback of these inductive machines is that they draw a huge amount of Reactive Power (KVAr) from supply side, thus causing lowering of Power Factor (P.F.).
- Power Factor:
Power Factor is defined as ratio of Real Power (expressed in Watts) to Apparent Power (measured in Volt-Ampere VA). The Real Power is what is actually delivered and consumed by the electrical device. Thus, lower the value of Real Power, lower will be the Power Factor.
An ideal case Power factor has to be 1.0 however, it is practically impossible to equate Real Power to Apparent Power therefore, at practical levels the equipments operate at a Power Factor of 0.9 to 0.95.
A fall out of this low Power Factor is that it puts a burden on the electrical supply side, as this forces the utility to generate more power (KVA) than its required size.
By installing a Shunt Capacitor, it ensures that the reactive Power (KVAr) in the system is compensated locally with its own KVAr rating. Thus, it prevents the varying reactive power demands hitting the supply side and eventually protects the supply side equipments (transformers, generators etc.)
It is a common practice by utility companies to charge penalties to consumers who fall below the set benchmark value of Power Factor. For large Industrial consumers this may mean a huge financial impact. Hence, electrical managers and designers always keep a special eye on operating conditions of Power Factor and try to compensate it with appropriate sized Capacitors installed.
Installation of a Shunt Capacitor
Shunt Capacitors are installed closer to the inductive load side.
The capacitors may energized continuously or switched on and off during load cycles.
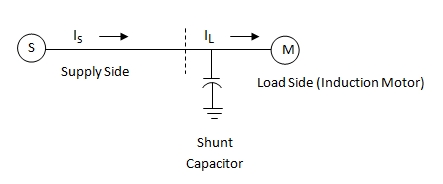
Figure below shows a circuit with Shunt capacitor applied at load side:
As seen in figure above, the shunt capacitor is connected nearer to inductive load (Induction motor in this case). Depending on the type of capacitor chosen, it may be fixed or switched operation capacitor and provides Reactive power compensation (VAR) at the load side, thus preventing the Supply side from getting affected.
Benefits of Reactive Power Compensation using Shunt Capacitor
- Increased System Capacity – As the installed Shunt Capacitor improves the power factor and reduces circuit current for given load, therefore a greater KVA can be carried to the load before enhancing the supply side.
- Improved Voltage conditions – Since Reactive power is better managed, it does not cause voltage fluctuations at feeder level, and thus, there is a good balanced load condition prevailing in the circuit
- Reduction in Power System Losses – Use of shunt capacitor improves Power Factor and reduces the currents, it also causes the associated I2R losses to go down. Thus there is a reduction in Power system losses.
- Reduced Energy Bill and Avoiding Penalties – A higher power factor keeps the monthly energy bill down and thus helps possible penalties by the utility company due to crossing of set Power factor limits.
Do you agree with my vision of the use of capacitors in electrical circuits? Let’s talk about it and thanks for reading.
Dear Sir;
1200 KW load , how i can going to calculate and install the Shunt capacitor .