
However, the intermittence of this type of generation is its main limitation, given that the radiation received depends on atmospheric conditions.
In order to achieve the desired expansion of the market, new technologies have been developed to increase productivity, efficiency and generate economies of scale that will considerably reduce costs.
This article will approach some technological advances that use ingenuity to expand the use of this energy, take it to new scenarios and improve its performance.
Solar Energy: Solar Road
They are novel structures for the circulation of vehicles, built with photovoltaic panels, allowing the generation of electricity through the use of sunlight.
The first project built was a solar cycle of 70 meters, inaugurated in Krommenie-Holland at the end of 2014 (see image N ° 1). Elaborated with photovoltaic cells integrated into concrete and covered by a double layer of tempered glass as protection.

Image No. 1 Solar Road Cycle Located in Krommenie, Holland | source image @haimaneltroudi
This work exceeded the expectations of its creators because one year after its commissioning it generated 70 kWh per square meter, enough energy to power three houses.
In turn, the first solar road was inaugurated in Normandy-France in December 2016, using pavement formed by photovoltaic panels that support the weight of any type of vehicle, guaranteeing the adherence of the tires.
This road has a kilometer length covered with 2,280 panels, consisting of five layers of silicon to ensure resistance and generate electricity to power the public lighting of the town (image No. 2).

Image No. 2 Solar Road Located in Normandie, France | source image @haimaneltroudi
Likewise, China was not far behind, by the end of 2017 it inaugurated its solar road of 2 km in length (image N ° 3), located in the city of Jinan, capital of Shandong, near a substation to connect with the network.

Image No. 3 Solar Road Located in Jinan China | source image @elcomercio.pe
This road stands out as one of the most advanced in the world because it is manufactured by three layers; the first of transparent concrete, the second incorporates more than 10,000 photovoltaic panels and the third layer protects the panels from moisture.
The objective of this project is to charge electric vehicles when they are in motion, thanks to its system of coils by magnetic induction, which even serves to melt snow and accumulated ice.
It is worth mentioning that in April 2018, the company responsible for the work reported that the section generated more than 96,000 kWh of electricity in three and a half months.
Currently, five roads with this technology have been installed in countries such as France, Japan, China, the United States, and the Netherlands, thus showing the advances in this regard.
However, its production has not yet been massified, since its main obstacle has to do with economic investment. Experts claim that each kilowatt cost 17 euros, while the price of the photovoltaic installation on a roof is 1.3 euros in 2016.
Solar Energy: Solar Mechanical Cloud
It is a large device capable of capturing solar radiation acting as an artificial cloud, producing shade and regulating high temperatures in open spaces of large dimensions.
It was developed by scientists of the University of Qatar with the purpose of being used in the football stadiums of their country for the world championship of the year 2022, as shown in image N ° 4.

Image No. 4 Solar Mechanical Cloud | source image @BBC
It is constructed of a very light carbon fiber material, filled with helium for easy lifting through four turbines similar to a drone, they are powered by solar energy and managed through remote control to automatically follow the solar movement, maintaining the generation of shadow over the objective.
Although it is a development for a specific use it can have many other climatic applications in agriculture, energy saving, etc. This makes it a technology with a great perspective.
Solar Energy: Solar Bike
It is a bicycle that has an electric motor attached to help it to advance, which is powered by a battery (autonomy between 30 and 70 km) rechargeable by photovoltaic technology, being an alternative to the motorcycle or the car to travel medium distances (image N ° 5).

Image N ° 5 Solar Bike | source image @ecologiaverde
There are several companies that have developed such technology. Highlighting the creator of the bicycle “Velosphere E-Bike” (image No. 6), which becomes a high-efficiency photovoltaic panel when it’s stopped, deploying a kind of elliptical tent, ideal to maximize the capture of light.

Image N ° 6 Solar Bike Velosphere E-Bike | source image @glipp
Similarly, a company from Singapore has created a bicycle, called EHITS (Energy Harvesting Intermode Transport System) capable of generating solar and wind energy thanks to the installation of a photovoltaic panel in the frame and two wind turbines in the wheels (image N ° 7 ).
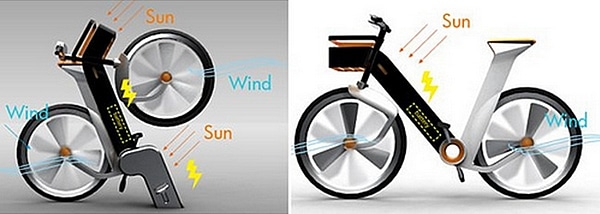
Image N ° 7 Bicycle Solar Energy Harvesting Intermode Transport System | source image @energialimpiaparatodos
Therefore, the models of solar bicycles are becoming increasingly interesting since they provide greater comfortability to users. This means that eventually, the ecological means of transport will end up evolving in the photovoltaic sector as well.
It is evident that the ingenuity applied in this field has no limits and we can expect many advances as there is a greater interest and investment in the area.
Thanks for reading this article.
What’s your impressions on these futuristic solar technologies? Do you think solar energy is the future?
Dear writer
While appreciating about your valuable article I have to inform you there is a tiny mistake in your article.
Regarding to following link, 70 kWh per square meter is not true and must be replaced with 70 kWh/m²/year.
Obviously 70Kwh/m² is too much for solar panels. As I know the best solar panels at the Ideal state, can generate power around 0.3~0.4 Kwh/m².
Please Let me know If I wrong.
Best regards.
Abbas mohseni
https://www.solaroad.nl/wp-content/uploads/2015/10/SolaRoad_UK.pdf