
Electrical power is transmitted through either overhead power lines or underground cables. Each of the two types of cables has its benefits as well as pitfalls as well as places where it is commonly used.
The choice of which method to use is influenced by voltage, cost, safety, type of application, and other factors. Whereas, the overhead lines are cheap, easy to install, troubleshoot and upgrade, the same cannot be said about the underground cables. Underground cables have their place too, and despite being expensive, they have several advantages. These are mostly used where it is dangerous to have overhead lines such as densely populated areas as well as in providing the missing link in areas where overhead lines cannot be used.
Due to cost, physical and environmental factors, the two types of cables are usually combined together in most situations. To understand how the two cable types differ from one another, below are the notable differences between the two.
A comparison between underground and overhead transmission cables:
Construction
Underground cables are more expensive to construct since they have to be electrically insulated and have protection against moisture, corrosion, mechanical damage and other environmental impacts from the soil. Construction of the cables is more complicated compared to the overhead cables which are simple to construct, and do not require insulation and sheathing. The overhead cables have lesser requirements and cheaper to construct.
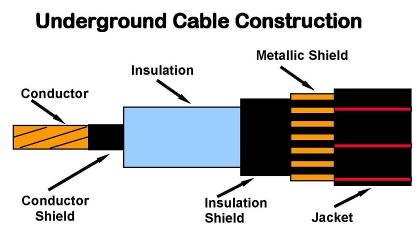
Figure 1: Underground cable construction |image: http://www.pesicc.org
Installation
The installation of overhead lines on poles is easier and straightforward. However, the underground cables require digging trenches and this may be complicated by other utility service lines such as water pipes, oil and gas pipelines, sewer lines. Other complications may arise due to rocks, loose soil and water along the routes, making them more expensive to install.
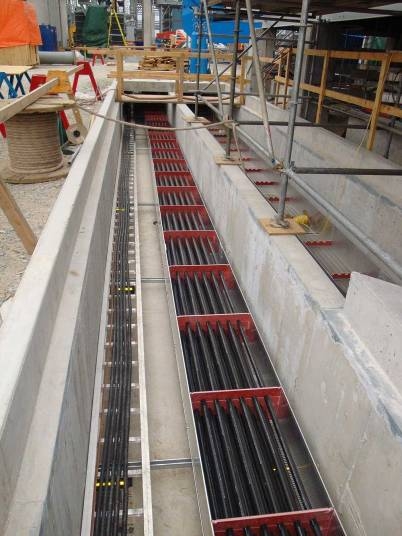

Figure 2: Underground cable system | image: powerbusway.com
Heat dissipation
Heat dissipation in underground cables is limited by the layers of insulation and protection such as armoring and sheaths. Most of the heat is therefore retained near the cable unlike the overhead cables where most of the heat is released to the surrounding and automatic natural cooling is provided by the air.
Size of Conductors
Underground cables have larger conductor sizes compared to overhead lines for the same amount of power. This is due to the fact that the overhead lines have a natural cooling and hence the ability to carry more power without heating up.
Voltage carrying capacity
The overhead lines are better suited to carry higher voltages compared to the underground cables, which are limited by the expensive construction and limited heat dissipation. For these reasons, the underground cables are mostly used for transmitting up to 33KV.
Fault detection and repair
It is easier to detect and repair faults in overhead cables. It is more complicated and takes more time to locate and repair the underground systems.
Public safety
Underground cables are safer to the public, animals and environment compared to the overhead lines i.e. there are no issues such as people getting in contact with fallen lines. The overhead cables can be brought down and human, animal intervention, weather as well vegetation such as trees.
The underground cables are less impacted by these conditions and not affected by trees, animals, accidents, wind, storms and other physical interference that may lead to broken poles and short circuits or cable breakages.
Effect of lightning discharges
Overhead cables are more prone to lightning strikes whereas the underground cables are not affected by the discharges.
Interference
Overhead lines interfere with communication lines that are in close proximity, have corona discharge, radio and TV interference which does not happen with the underground lines.
Voltage drop
There is more voltage drop in the overheads due to the fact that their cables are of much smaller diameter than underground cables for the same power delivery.
Environmental impact
The underground cables have more environmental and health benefits due reduced noise and better vegetation management. In addition, they have less transmission losses, reduced damage and accidents such as wildlife electrocutions.
On the other hand the overhead cables can be brought down by human, animal intervention, weather such as strong winds and storms, as well vegetation such as tall trees. The underground cables are less impacted by these conditions and have less visual impact.

Figure 3: Overhead transmission cables | image mirror.co.uk
Land use
The underground cables allow better use of land coupled with better views without the sight of poles and cables. This leads to improved property values.
Life expectancy
Overhead lines have a longer life span compared to undergrounds cables.
Conclusion
The underground cables are more expensive to construct and install, however, they are convenient, less likely to break and mostly used to provide the missing link where overhead cables cannot be used. The choice of the cable to use is determined by the particular situation. The overhead cables are widely used due to their cost and ability to carry more power compared to the underground.
Thank you for reading my material,
A.N.
Nice article! Did you find this comparison useful? Do you agree? Which other differences do you see between the two?
The overhead cables are exposed to so many risks due to direct contacts and expansions due heat